Main enamel, child enamel, milk enamel, deciduous enamel, non permanent enamel…
There are numerous names on your child’s first enamel. Whereas main enamel improvement most frequently follows a sure sequence, variations can occur, and it’s good to concentrate on whether or not the event you see in your little one is regular or one thing {that a} dentist or pediatrician ought to deal with.
On this article, we undergo regular and irregular enamel improvement and reply widespread questions dad and mom have about their younger youngsters’s enamel.

When Do a Child’s Tooth Develop?
Tooth improvement happens earlier than delivery. It begins with the formation of a “bud” throughout the fetal gum tissue at six weeks gestation. A central space of this tissue thickens to type what is named a tooth “bud”, which continues to develop right into a construction that may change into the middle of a brand new tooth. The center and outer tooth layers develop round this central space at 12 to 16 weeks gestation.
The Anatomy of a Tooth
A tooth consists of 4 layers: enamel, dentin, pulp, and root. Tooth are located throughout the gums of the higher jaw (maxilla) and decrease jaw (mandible).
Enamel
That is the outermost tooth layer, seen as a tough, white overlaying. Enamel is the toughest substance within the human physique.
Dentin
This layer lies simply beneath the enamel and surrounds the pulp. It’s the majority of a tooth’s construction.
Pulp
This central portion of a tooth homes the nerves and blood vessels. It additionally incorporates the parts wanted for the dentin layer. When tooth ache develops, it originates from the pulp.
root
The foundation is the pointed part of the tooth, imbedded into the gums. It secures the tooth to the jaw bone. The entrance enamel have one root, whereas bigger enamel might have two or three roots.
Calcium and phosphorus are the minerals essential for forming enamel and dentin. With out sufficient calcium throughout enamel improvement, magnesium and sodium change into the first parts, leading to much less sturdy enamel.
Regular Main Tooth Eruption
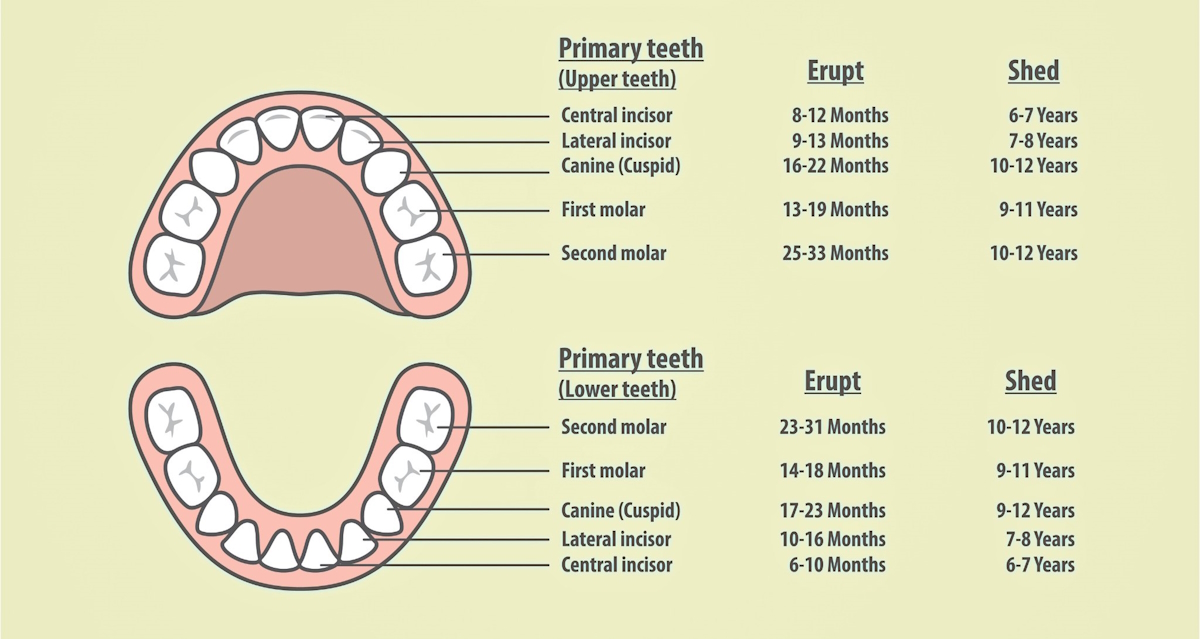

The above chart of the first enamel reveals each regular child enamel eruption and shedding.
For many infants, the primary tooth seems between ages six to 12 months. Earlier than this, there could also be signs of teething, comparable to elevated drooling or gnawing on fingers and objects. Discomfort from the stress of the erupting tooth in opposition to the gums is widespread. Infants could seem significantly uncomfortable when molars or a couple of tooth erupts without delay.
Main enamel normally erupt in a particular sequence: incisors first, then the primary set of molars, then the cuspids, after which lastly the second set of molars.
incisors
The entrance higher and decrease enamel are often called incisors. They’re used to chunk into meals, however infants might use them to chew earlier than different enamel erupt. The incisors are normally the primary enamel to look.
| Incisors Eruption Order | Youngster’s Age |
|---|---|
| Center decrease incisors | 6-10 months |
| Center higher incisors | 8-12 months |
| Lateral decrease incisors | 10-16 months |
| Lateral higher incisors | 9-13 months |
Cuspids
These are additionally known as the “canine” enamel due to their pointedness. Cuspids are positioned lateral to the incisors and normally erupt after the primary molars.
| Cuspids Eruption Order | Youngster’s Age |
|---|---|
| Decrease cuspids | 17-23 months |
| Higher cuspids | 16-22 months |
Molars
The molars are the bigger enamel behind the mouth which might be necessary for chewing meals. The primary set sometimes erupts after the incisors. The second molars are the ultimate main enamel to erupt, normally after the second birthday.
| Molars Eruption Order | Youngster’s Age |
|---|---|
| First decrease molars | 14-18 months |
| First higher molars | 13-19 months |
| Second decrease molars | 23-31 months |
| Second higher molars | 25-33 months |
A number of months might cross between the looks of the cuspids and second molars. Your toddlers (and we, dad and mom) get a much-needed break from the discomfort of teething throughout this section. If a two-year-old out of the blue develops crankiness and begins to drool once more, it’s probably that the second molars will quickly erupt.
In the end, there needs to be a whole of 20 main enamel.
Abnormalities in Tooth Eruption
Natal and Neonatal Tooth
Can infants be born with enamel?
Sure, there are uncommon events the place a number of enamel are current already at delivery. In different instances, neonatal enamel erupt throughout the first 30 days of life. Though the precise trigger is unknown, such early enamel eruption is regarded as the results of some kind of prenatal stress.
Most natal or neonatal enamel are the decrease incisors. They’ll trigger trauma to the toddler’s tongue whereas feeding and trigger ache for breastfeeding moms.
These early enamel could also be an remoted discovering or one in all many options of a genetic syndrome. In the event that they change into unfastened, they’re an aspiration threat. Except this can be a concern or an toddler can’t feed, extraction is mostly not advisable.
Congenitally Absent Tooth
There are occasions when main enamel fail to develop throughout fetal life. This turns into obvious when some enamel are lacking, as others erupt.
The absence of main enamel could also be as a result of genetics; a guardian might have had the identical problem as an toddler. Lacking enamel are sometimes related to chromosomal abnormalities comparable to Down syndrome and others. Prenatal publicity to maternal infections, sicknesses, or sure medicines might also be the trigger.
Whether or not or not intervention is important depends upon the variety of lacking enamel and its impact on the kid’s high quality of life. If many enamel are absent, partial dentures could also be advisable if age-appropriate.
Delayed Tooth Eruption
Worrying that your baby has no teeth yet is widespread amongst dad and mom. Nevertheless, the timing of tooth eruption can range by gender, race, and ethnicity. If there are no enamel by the primary birthday or all 20 enamel haven’t appeared by age 4, this warrants an analysis by a dentist.
There are numerous explanation why some enamel might take longer to erupt than others:
Gum/Gingiva Issues
If there may be an abnormality on the floor of the gums, this will impede tooth eruption. Thickened gums as a result of prenatal publicity to sure medicines or maternal vitamin C deficiency can block the trail of tooth eruption.
If there’s a tumor, scar tissue, or different defect, this will create a barrier. Nevertheless, a blood vessel that overlies an erupting tooth shouldn’t trigger interference. Because the tooth pushes previous this blood vessel, there could also be a small quantity of bleeding underneath the gums, famous as a bluish discoloration. This phenomenon is regular and sometimes doesn’t have an effect on the tooth itself or the timing of its eruption.
Issues with Tooth Growth
If the inside tooth dentin fuses to the jaw bone throughout fetal improvement, that tooth can’t erupt.
Prematurity and Low Beginning Weight
Infants born before 30 weeks gestation and/or with a delivery weight under 1000g are in danger for delayed tooth maturation and eruption. Infants who’re small for gestational age or don’t develop sufficiently in utero are additionally in danger.
Dietary Components
Delayed tooth eruption might happen if an toddler doesn’t obtain adequate vitamins through the placenta or after delivery. The incidence is greater in communities the place entry to nutritious meals is restricted. Breastfeeding is regarded as preventative.
Medical Circumstances
Along with genetic syndromes, some toddler and childhood medical situations can delay enamel eruption. These embrace congenital HIV an infection, hypothyroidism, pituitary dysfunction, cerebral palsy, anemia, and kidney illness.
Problems Related to Irregular Tooth Shapes or Colours
A number of medical situations famous at delivery may end up in irregular main enamel. They might be related to different bodily abnormalities, so early detection is necessary. A few of these youngsters require multidisciplinary care all through their lives.
Congenital Syphilis
Over 130,000 instances of syphilis have been reported within the U.S. in 2020, and the numbers proceed to extend. Syphilis is a sexually acquired an infection that may be transmitted to a fetus through the placenta.
Amongst different facial abnormalities, syphilis can impair fetal tooth improvement, leading to Hutchinson Tooth. When enamel erupt, they’re slim and have notches.
Amelogenesis Imperfecta
The enamel fails to type correctly in infants with amelogenesis imperfecta. Due to inadequate calcium and phosphorus throughout the enamel, enamel have a yellow or brown discoloration.
This situation could also be the results of an an infection, vitamin D deficiency throughout being pregnant, or a genetic mutation.
As soon as erupted, the enamel are fragile, crack continuously, and are vulnerable to decay. Along with beauty challenges, there could also be sensitivities to temperature and sure meals.
Ectodermal Dysplasia
Ectodermal dysplasia might be inherited from a guardian or as a result of a genetic mutation. It’s characterised by poorly developed hair, pores and skin, enamel, and nails.
Tooth are small, globe-shaped, or extensively spaced. Some main enamel could also be absent. Growth of tooth enamel can also be affected, which will increase the chance of tooth decay.
Tetracycline Tooth
Prenatal publicity to tetracycline and related antibiotics could cause staining of fetal enamel. These antibiotics are used to deal with sicknesses comparable to Lyme illness, sexually transmitted infections, and resistant Staphylococcus (MRSA). The remedy accumulates throughout the “tooth bud,” and binds to calcium, forming dark-colored areas throughout the dentin and enamel.
Publicity to Chemotherapy
Pregnant moms present process most cancers therapy with sure chemotherapeutic medication might have infants with discolored enamel. If therapy is initiated throughout the first trimester, the scale of the main enamel could also be smaller than anticipated.
Hyperbilirubinemia
Jaundice, a yellow coloring of an toddler’s pores and skin, is widespread throughout the first week of life. It’s attributable to the blood pigment bilirubin deposition into the pores and skin and eyes. If famous throughout the first few days of life, the bilirubin degree is checked on the hospital. Bilirubin ranges above 15 require intervention to forestall additional elevation that would hurt an toddler’s mind.
Excessive bilirubin ranges are additionally related to a inexperienced discoloration of enamel. This is because of bilirubin deposition into the dentin.
Retaining Toddler and Toddler Tooth Wholesome

Though generally not prioritized, oral care is necessary to toddler and toddler well being. Even earlier than enamel erupt, dad and mom ought to gently clear their child’s tongue with a moist washcloth to lower milk accumulation and wipe the gums as soon as pureed meals are launched.
After the primary enamel erupt, dad and mom ought to start to brush them at bedtime. Incisors could also be simply cleaned with an over-the-finger sort of toothbrush, however a handle-type one is suitable as soon as molars erupt.
Fluoride
Fluoride helps to harden tooth enamel and is essential for cavity prevention. Though there are various fluoride-free toothpastes out there available on the market, each the American Dental Affiliation and the American Academy of Pediatrics suggest fluoride toothpaste for all ages:
| Age | Quantity of toothpaste |
|---|---|
| Ages 6 months to three years | “grain of rice”-sized smear of toothpaste |
| Ages 3 years and up | “pea-sized” quantity of toothpaste |
Kids over age two might be taught to spit out the toothpaste. These fluoride suggestions are based mostly on rising charges of cavities and poor oral well being amongst youngsters.
For communities with out native water fluoridation, prescription fluoride supplements are recommended. These are taken each day and are dosed based mostly on age:
| Age | Fluoride complement quantity |
|---|---|
| Ages 6 months to three years | 0.25mg fluoride/mL |
| Ages 3 to six years | 0.5mg fluoride/mL or tablets |
| Ages 6 and up | 1mg fluoride tablets |
Mother and father ought to contact their municipality to find out if fluoride is included of their native water therapy course of.
Dental Visits
The American Dental Affiliation recommends that infants see a dentist after the primary tooth erupts between ages six to 12 months. This isn’t a go to for a dental cleansing however to evaluate for potential issues. For instance, some infants are born with a distinguished connective tissue between the higher lip and central incisors. This could make it tough to maintain the higher enamel clear and enhance the chance of dental caries.
Routine dental visits are advisable each six months. As soon as all enamel have erupted, dental cleanings might start.
Apart from routine care, dad and mom ought to take their child to a dentist if the enamel seem irregular upon eruption. A dental analysis needs to be a part of the care plan if an toddler is born with a medical situation that may have an effect on the enamel.
If no enamel have erupted by 13 months, or some enamel are nonetheless lacking at age 4, additional analysis is important.
Mother and father’ Widespread Questions About Main Tooth Growth
My child’s enamel are “coming in crooked.” What ought to I do?
It isn’t uncommon for an toddler to have just a few enamel which might be misaligned. That is usually as a result of household historical past. Most instances usually are not related to secondary enamel issues or misalignment.
The infant ought to see a dentist if misaligned enamel trigger cheek or lip trauma whereas consuming.
Why are my child’s prime entrance enamel not coming in? Is it regular for enamel to come back in out of order?
Some toddler enamel deviate from the standard eruption order, for instance, getting the lateral incisors earlier than the central ones. Usually, this isn’t a trigger for concern. Nevertheless, dad and mom ought to converse to a dentist if the central enamel fail to erupt after just a few months whereas others seem.
My child’s enamel look malformed. What ought to I do?
In case your child’s enamel appear irregular in form, measurement, or colour, you must converse to your pediatrician and dentist. Some tooth issues are related to different medical issues that must be addressed. Your child’s dentist can clarify why the abnormalities have occurred and what might be carried out.
Why does my child have mottled enamel, and what ought to I do?
“Mottled” is a common description for enamel which have white, yellow, or brown spots, generally with a faulty floor. There are a number of causes that enamel might develop mottling, so you must focus on this with a dentist.
One doable trigger is the ingestion of an excessive amount of fluoride. This generally happens when extreme fluoride is current in consuming water. No greater than 0.07mg/kg of fluoride needs to be ingested each day to forestall tooth fluorosis. Mother and father ought to pay attention to the fluoride content material of their native water sources.
Is it regular for a 12 to 15-month-old to haven’t any enamel?
At 12 months, some toddlers are simply getting their first two enamel, which is comparatively late however nonetheless throughout the regular vary.
Nevertheless, suppose there is no such thing as a signal of impending eruption (swollen gums with underlying enamel imprints). In that case, the toddler needs to be evaluated for doable lacking enamel or a gum downside. 13 to 15-month-olds with out enamel additionally want additional analysis.
Takeaway
Usually, a child’s main enamel improvement will observe the anticipated route, and the enamel that erupt will likely be wholesome and look regular. On this case, the one issues we dad and mom must do are to make sure cautious enamel care and assist our youngsters with their teething ache.
Nevertheless, it is very important pay attention to the irregular main enamel improvement that may happen and seek the advice of a pediatric dentist with any worries.
Learn Subsequent
Analysis References
- John Hopkins Drugs:The anatomy and development of the mouth and teeth
- Morris AL, Tadi P. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Teeth. [Updated 2023 Jul 24]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-.
- Srđan Nedoklan, Zlatka Knezovic, Nina Knezovic, Davorka Sutlovic, NUTRITION AND MINERAL CONTENT IN HUMAN TEETH THROUGH THE CENTURIES, Archives of Oral Biology, Quantity 124, 2021.
- Newadkar, Ujwala Rohan1,; Chaudhari, Lalit1; Khalekar, Yogita Okay.1. Natal and neonatal teeth: Terminologies with diverse superstitions!!. Journal of Household Drugs and Main Care 5(1):p 184-185, Jan–Mar 2016. | DOI: 10.4103/2249-4863.184663


Paula Dennholt based Straightforward Child Life in 2006 and has been a passionate parenting and being pregnant author since then. Her parenting method and writing are based mostly on research in cognitive-behavioral fashions and remedy for kids and her expertise as a mom and stepmother. Life as a guardian has satisfied her of how essential it’s to place relationships earlier than guidelines. She strongly believes in constructive parenting and a science-based method.
Paula cooperates with a team of pediatricians who help in reviewing and writing articles.
Trending Merchandise












